Product Description
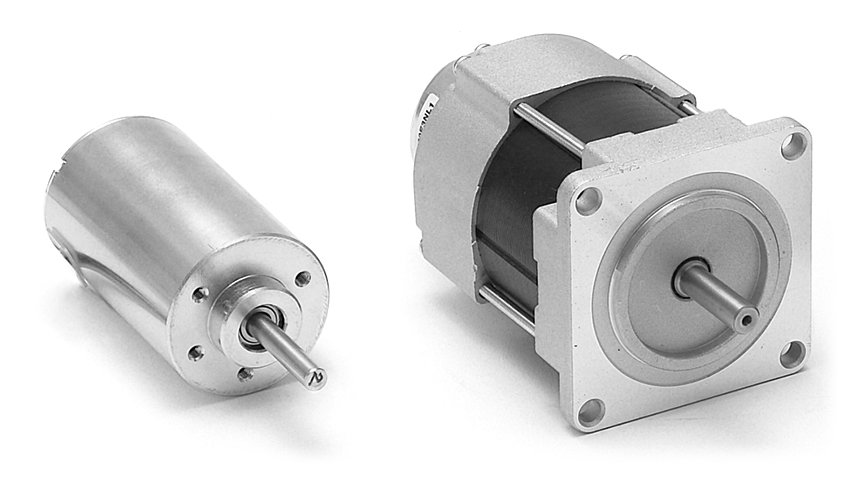
SZGH-09075BC AC Servo motor with driver 220V 750W 2000R 3.5N dc motor and driver for CNC machine
SZGH-09075BC is 750W servo motor ,optimizing design, compact, beautiful contour, long-term continuous working in rated working mode and economic type
Packing list :
1) SZGH-09075BC 750w servo motor -1pcs
2) SZGH-SD2571 220v servo driver – 1pcs
3) SZGH1MX-5M 5meter motor cables -1pcs
4) SZGH1EX-5M 5 meter encoder cables -1 pcs
5) Manual -1pcs
Pls tell us at first time when you need :
1) Brake motor
2) 2500PPR encoder
3) long cables
Product Description
|
Rated Power |
750W |
|
Rated torque |
3.5NM |
| Rated Speed | 2000RPM |
|
Rated Curret |
3A |
|
Rated Voltage |
220V |
|
Encoder |
2500PPR/17bit/23bit |
Description of Driver
Input Power :
Single Three Phase AC220V-15%~+10% SO/60HZ
Control model :
0: Position Control; 1:Speed Control;
2: Torque Control; 3:Position/Speed Control;
4·PositionTorque Control: 5:Speed Torque Control
Protective Function :
Over-speed Over-voltage Under-voltage Over-current OverloadEncoder Error/ Control Power Eror/ Position Offset Eror
Driver Load : Less than 3times of rotor inertia
Display : 5 bits LED indicator display 4 Operate keys
Communication : RS485
Position Control : Input Model , Electric Ratio
Product Parameters
| Power(W Torque(N.m) Speed (rpm) | |||||
| Flange | Model | Matched Servo Drive | |||
| 40mm | SZGH-04005D | 50 | 0.16 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2004 |
| SZGH-5711D | 100 | 0.32 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2004 | |
| 60mm | SZGH-06571DC | 200 | 0.6 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2004 |
| SZGH-06040DC | 400 | 1.3 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2004 | |
| SZGH-06060DC | 600 | 1.9 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2004 | |
| 80mm | SZGH-08040DC | 400 | 1.3 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2571 |
| SZGH-08075DC | 750 | 2.4 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2571 | |
| SZGH-08075BC | 750 | 3.5 | 2000 | SZGH-SD2571 | |
| SZGH-5710CC | 1000 | 4 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2571 | |
| 90mm | SZGH-09075DC | 750 | 2.4 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2571 |
| SZGH-09075BC | 750 | 3.5 | 2000 | SZGH-SD2571 | |
| SZGH-5710CC | 1000 | 4 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2571 | |
| 110mm | SZGH-11060DC | 600 | 2 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2026 |
| SZGH-11080DC | 800 | 4 | 2000 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH11120DC | 1200 | 4 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH-11150DC | 1500 | 5 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH-11120BC | 1200 | 6 | 2000 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH11180DC | 1800 | 6 | 3000 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| 130mm | SZGH-13100CC | 1000 | 4 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2026 |
| SZGH-13130CC | 1300 | 5 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH-13150CC | 1500 | 6 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH-13200CC | 2000 | 77 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2026/SZGH-SD4038(380V) | |
| SZGH-13100AC | 1000 | 10 | 1000 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH-13150AC | 1500 | 10 | 1500 | SZGH-SD2026 | |
| SZGH-13230AC | 2300 | 15 | 1500 | SZGH-SD2026SZGH-4038(380V) | |
| SZGH-13260CC | 2600 | 10 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2026/SZGH4038(380V) | |
| SZGH-13380CC | 3800 | 15 | 2500 | SZGH-SD2026/SZGH-4038(380V) | |
| SZGH-15380CC | 3800 | 15 | 2500 | SZGH-4038 | |
| SZGH-15300BC | 3000 | 15 | 2000 | SZGH-4038 | |
| SZGH-15360BC | 3600 | 18 | 2000 | SZGH-4038 | |
| SZGH-1S470BC | 4700 | 23 | 2000 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-15550BC | 5500 | 27 | 2000 | SZGH-4075 | |
| 1 80mm | SZGH-18270BC | 2700 | 17.2 | 1500 | SZGH-4075 |
| SZGH-18290BC | 2900 | 27 | 1000 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-18300CC | 3000 | 19 | 1500 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-18370BC | 3700 | 35 | 1000 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-18430AC | 4300 | 27 | 1500 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-18450CC | 4500 | 21.5 | 2000 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-18550CC | 5500 | 35 | 1500 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SZGH-18750CC | 7500 | 48 | 1500 | SZGH-4075 | |
| SD Series | SD2004 | SD2571 | SD2026 | SD4038 | SD4075 |
| Output Power | 50W~600W | 400W~1kW | 600W~3. 8kW | 2kW~3 8KW | 3kW~75kW |
| Input Power | Single/Three Phase AC220V-15%~+10% 50/60Hz |
Three Phase 380V | |||
| Control Mode | 0. Position Control: 1 Speed Control; 2: Torque Control: 3:Position/Speed Control; 4:PositionT orque Control: 5:SpeedTorque Control |
||||
| Protective Function |
Over-speed/Over-voltageUnder-voltage Over-current/Overload/Encoder Error/ Control Power Eror/ Position Offset Enor |
||||
| Monitor Function | SpeedPositionPulses /Offset/TorqueCurrent/Status. | ||||
| Digital Input | 1:Servo Enable: 2:Alam Reset: 3:CCW-Forbidden: 4:CW-Forbi dden: 5:Clear Position Ofiset; 6:Pulse Input Forbidden; 7:CCW Torque Limit: 8:CW Torque Limit |
||||
| Digital Output | Servo-Ready On/Alam/ Orientation EndBraker Control | ||||
| Energy Braking | Support buit in Extemal Resistor Braking | ||||
| DriveLoad | Less than 3 times of rotor inertia | ||||
| Display | 5 bits LED Indicator display: 4 Operate keys | ||||
| Communication | RS485 | ||||
| Position Control | Input Mode | 0: Pulse+Direction | |||
| 1:CCW/CW Pulse | |||||
| I . . 2: AB Phase Orthogonal Pulse | |||||
| 1 . 1 3:Inner Position Control | |||||
| Electic Ratio | Numerator of Electric Ratio: 1~32767 | ||||
| Denominator of Electric Ratio: 1~32767 | |||||
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
1.Industrial packing: plastic bag +foam boxes+ carton +wooden pallets
2.Commercial packing: plastic bag+ foam boxes + carton
3.As the clients requirement
Delivery Detail: Normally ready goods and stock within 2- 5days
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG Automation CO.,LTD
(Formerly known as ‘HangZhou CHINAMFG Automation Co.,Limited(Built in 19 November 2571)’)
We are 1 of the leading Ce in CNC package solution, Our focus has been on providing the high quality of Industrial robot arm LNC & automatic company in China, specialized in designing projects, marketing, and oversea trading, having extensive experiencathe CNC system, Milling CNC system, Engraving CNC system, Grinding & router CNC system, Motor & driver, Spindle servo motor & driver, Gear reducer and Robot arm.
SZGH’ products have been in working with a wide variety of CNC machinery and automatic processing equipment with high performance and good precision, stably. We have now established a reliable structure , our experienced engineers and technicians are able to provide professional consultancy and offer you most suitable CNC application solution.
Our strict quality control measures guarantee excellent reliability and high standard of quality. Utilizing advanced CNC machinery to test every product, 100 percent inspection is made before packaging and shipment. Moreover, We also offer flexible lead times to support your business.
We have a large number of customers across Asia, America, the Middle East, Europe, South America, and Africa. Specially we already built own business corporate group in Middle East market.
Our Advantages
After Sales Service
|
Best & Professional after- sales supports
Our company have very professional engineers teams ; We can provide the professional after -sales service to our all clients ; Here is our engineer Mike solved the problems for our customer ; Best supports !! Quicly reply !! Buy at ease , use at ease !!! |
FAQ
Q: Do you support customized manufacturing?
A: Yes,we can customized manufacturing according to customer’s requirment. We support to OEM your own company display interface and logo.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 3-5 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 5-10 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to
quantity.10-20 days if customized manufacturing.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample with sample price.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment=1000USD, 70% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
If you have another question, pls feel free to contact us as below
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machine Tool |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Variable Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving, Control |
| Casing Protection: | Explosion-Proof Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How does the speed control of a DC motor work, and what methods are commonly employed?
The speed control of a DC (Direct Current) motor is essential for achieving precise control over its rotational speed. Various methods can be employed to regulate the speed of a DC motor, depending on the specific application requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of how speed control of a DC motor works and the commonly employed methods:
1. Voltage Control:
One of the simplest methods to control the speed of a DC motor is by varying the applied voltage. By adjusting the voltage supplied to the motor, the electromotive force (EMF) induced in the armature windings can be controlled. According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, the speed of the motor is inversely proportional to the applied voltage. Therefore, reducing the voltage decreases the speed, while increasing the voltage increases the speed. This method is commonly used in applications where a simple and inexpensive speed control mechanism is required.
2. Armature Resistance Control:
Another method to control the speed of a DC motor is by varying the armature resistance. By inserting an external resistance in series with the armature windings, the total resistance in the circuit increases. This increase in resistance reduces the armature current, thereby reducing the motor’s speed. Conversely, reducing the resistance increases the armature current and the motor’s speed. However, this method results in significant power loss and reduced motor efficiency due to the dissipation of excess energy as heat in the external resistance.
3. Field Flux Control:
Speed control can also be achieved by controlling the magnetic field strength of the motor’s stator. By altering the field flux, the interaction between the armature current and the magnetic field changes, affecting the motor’s speed. This method can be accomplished by adjusting the field current through the field windings using a field rheostat or by employing a separate power supply for the field windings. By increasing or decreasing the field flux, the speed of the motor can be adjusted accordingly. This method offers good speed regulation and efficiency but requires additional control circuitry.
4. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM):
Pulse Width Modulation is a widely used technique for speed control in DC motors. It involves rapidly switching the applied voltage on and off at a high frequency. The duty cycle, which represents the percentage of time the voltage is on, is varied to control the effective voltage applied to the motor. By adjusting the duty cycle, the average voltage across the motor is modified, thereby controlling its speed. PWM provides precise speed control, high efficiency, and low power dissipation. It is commonly employed in applications such as robotics, industrial automation, and electric vehicles.
5. Closed-Loop Control:
In closed-loop control systems, feedback from the motor’s speed or other relevant parameters is used to regulate the speed. Sensors such as encoders or tachometers measure the motor’s actual speed, which is compared to the desired speed. The difference, known as the error signal, is fed into a control algorithm that adjusts the motor’s input voltage or other control parameters to minimize the error and maintain the desired speed. Closed-loop control provides excellent speed regulation and accuracy, making it suitable for applications that require precise speed control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
These methods of speed control provide flexibility and adaptability to various applications, allowing DC motors to be effectively utilized in a wide range of industries and systems.
Are there specific types of DC motors designed for different industries or applications?
Yes, there are specific types of DC (Direct Current) motors that are designed and optimized for various industries and applications. DC motors offer a wide range of performance characteristics, allowing them to be tailored to specific requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the types of DC motors designed for different industries or applications:
1. Brushed DC Motors:
Brushed DC motors are commonly used in applications that require simple and cost-effective motor solutions. They are suitable for applications with lower efficiency requirements and where maintenance considerations are manageable. Some common industries and applications that use brushed DC motors include:
- Automotive: Power window mechanisms, windshield wipers, cooling fans, and seat adjustment systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Household appliances, toys, power tools, and personal care devices.
- Industrial Machinery: Conveyors, pumps, fans, and machine tools.
2. Brushless DC Motors:
Brushless DC motors are known for their higher efficiency, greater reliability, and precise control capabilities. They are widely used in industries and applications that demand higher performance and advanced control features. Some specific industries and applications that utilize brushless DC motors include:
- Automotive: Electric power steering systems, electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and HVAC systems.
- Aerospace and Defense: Actuators, robotics, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and missile systems.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Centrifuges, pumps, robotics, and diagnostic devices.
- Industrial Automation: CNC machines, robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and precision motion control systems.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbine generators, solar tracking systems, and energy storage systems.
3. High-Torque DC Motors:
High-torque DC motors are designed to provide substantial torque output at low speeds. They are commonly used in applications that require heavy lifting or high starting torque. Industries and applications that often utilize high-torque DC motors include:
- Material Handling: Cranes, hoists, winches, lifts, and elevators.
- Construction and Mining: Excavators, bulldozers, drilling rigs, and conveyor systems.
- Automotive: Electric vehicles, electric powertrains, and traction control systems.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Thrusters, winches, and anchor handling systems.
4. Low-Voltage DC Motors:
Low-voltage DC motors are designed to operate at lower voltages, typically below 24 volts. They are commonly used in battery-powered applications and systems where safety or specific voltage requirements exist. Some industries and applications that utilize low-voltage DC motors include:
- Automotive: Automotive accessories, window actuators, and door locks.
- Robotics and Hobbyist Projects: DIY robots, RC vehicles, and model trains.
- Solar Power Systems: Solar tracking systems, solar panel actuators, and solar-powered water pumps.
- Home Automation: Automated blinds, curtains, and smart home devices.
These are just a few examples of the types of DC motors designed for different industries and applications. The versatility and adaptability of DC motors make them suitable for a wide range of uses, and manufacturers often offer customized motor solutions to meet specific requirements.

How does the size and power rating of a DC motor affect its suitability for different tasks?
The size and power rating of a DC (Direct Current) motor play crucial roles in determining its suitability for different tasks and applications. The size and power rating directly impact the motor’s performance characteristics, including its torque output, speed range, efficiency, and overall capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the size and power rating of a DC motor affect its suitability for different tasks:
Size of DC Motor:
The size of a DC motor refers to its physical dimensions, including its diameter, length, and overall volume. The size of the motor influences its ability to fit into specific spaces or applications with space constraints. Here are some key considerations regarding the size of a DC motor:
1. Space Limitations: In applications where space is limited, such as small robotic systems or compact machinery, smaller-sized DC motors are preferred. These motors provide a more convenient and efficient integration into the overall system design.
2. Weight Constraints: Certain applications, such as drones or lightweight robots, may have strict weight limitations. Smaller-sized DC motors are generally lighter, making them more suitable for weight-sensitive tasks where minimizing the overall system weight is essential.
3. Cooling and Heat Dissipation: The size of a DC motor can impact its ability to dissipate heat generated during operation. Smaller-sized motors may have less surface area for heat dissipation, which can lead to increased operating temperatures. In contrast, larger-sized motors typically have better heat dissipation capabilities, allowing for sustained operation under heavy loads or in high-temperature environments.
Power Rating of DC Motor:
The power rating of a DC motor refers to the maximum power it can deliver or the power it consumes during operation. The power rating determines the motor’s capacity to perform work and influences its performance characteristics. Here are some key considerations regarding the power rating of a DC motor:
1. Torque Output: The power rating of a DC motor is directly related to its torque output. Higher power-rated motors generally provide higher torque, allowing them to handle more demanding tasks or applications that require greater force or load capacity. For example, heavy-duty industrial machinery or electric vehicles often require DC motors with higher power ratings to generate sufficient torque for their intended tasks.
2. Speed Range: The power rating of a DC motor affects its speed range capabilities. Motors with higher power ratings can typically achieve higher speeds, making them suitable for applications that require rapid or high-speed operation. On the other hand, lower power-rated motors may have limited speed ranges, making them more suitable for applications that require slower or controlled movements.
3. Efficiency: The power rating of a DC motor can impact its efficiency. Higher power-rated motors tend to have better efficiency, meaning they can convert a larger proportion of electrical input power into mechanical output power. Increased efficiency is desirable in applications where energy efficiency or battery life is a critical factor, such as electric vehicles or portable devices.
4. Overload Capability: The power rating of a DC motor determines its ability to handle overloads or sudden changes in load conditions. Motors with higher power ratings generally have a greater overload capacity, allowing them to handle temporary load spikes without stalling or overheating. This characteristic is crucial in applications where intermittent or varying loads are common.
Overall, the size and power rating of a DC motor are important factors in determining its suitability for different tasks. Smaller-sized motors are advantageous in space-constrained or weight-sensitive applications, while larger-sized motors offer better heat dissipation and can handle heavier loads. Higher power-rated motors provide greater torque, speed range, efficiency, and overload capability, making them suitable for more demanding tasks. It is crucial to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application and choose a DC motor size and power rating that aligns with those requirements to ensure optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China wholesaler DC Servo Motor Price 2kw 48V Brushless DC Motor 2500rpm a/c vacuum pump
Product Description
48V 1KW 2KW 3KW Robot Motor Brushless DC Servo Motor
Product Features
Protection grade:IP65, insulation grade:F
Winding overhang structure optimization, to minimize the copper loss and iron loss minimization, small volume, light weight, low temperature rise, high efficiency
Super high coercivity, the maximum magnetic energy product NdFe35 permanent magnetic materials, strong resistance to demagnetization, motor performance is stable.
Low noise, low vibration, low moment of inertia.
High torque, fast dynamic response, wide speed range, strong overload capacity (four times)
*High Torque to inertia ratio&up to 25000Nm/kgm²
*Fast dynamic response *time constant <20ms
*Wide speed adjusting&feedback up to 1000:1
*Steady speed precision up to 0.5%
*High overload,2Mn/30s,3.5N.m/10s
*Small volume and light
*Silent,the lowest noise is only 45dB(A)
*Protected with IP65,Class F insulation
Industry class
1.The altitude should be over 1000 CHINAMFG above sea level
2.Environment temperature:+5ºC~+40ºC
3.The month average tallest relative humidity is 90%,at the same the month average lowest temperature is less than 25
| Model | KY110AS0420-25 |
| VOLT | 48VDC |
| POWER | 2000W |
| SPEED | 1500RPM |
| TORQUE | 9.5N.M |
| ENCODER | 2500PPR |
| APPLICATION | AGV ROBOT,FIRE ROBOT,ELECTRIC VEHICLE |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Car, Electric Vehicle |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 10 |
| Samples: |
US$ 342/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
Brushed and brushless DC motors are two distinct types of motors that differ in their construction, operation, and performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors:
1. Construction:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors have a relatively simple construction. They consist of a rotor with armature windings and a commutator, and a stator with permanent magnets or electromagnets. The commutator and brushes make physical contact to provide electrical connections to the armature windings.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors have a more complex construction. They typically consist of a stationary stator with permanent magnets or electromagnets and a rotor with multiple coils or windings. The rotor does not have a commutator or brushes.
2. Commutation:
Brushed DC Motors: In brushed DC motors, the commutator and brushes are responsible for the commutation process. The brushes make contact with different segments of the commutator, reversing the direction of the current through the armature windings as the rotor rotates. This switching of the current direction generates the necessary torque for motor rotation.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors use electronic commutation instead of mechanical commutation. The commutation process is managed by an external electronic controller or driver. The controller determines the timing and sequence of energizing the stator windings based on the rotor position, allowing for precise control of motor operation.
3. Efficiency:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors tend to have lower efficiency compared to brushless DC motors. This is primarily due to the energy losses associated with the brushes and commutation process. The friction and wear between the brushes and commutator result in additional power dissipation and reduce overall motor efficiency.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors are known for their higher efficiency. Since they eliminate the use of brushes and commutators, there are fewer energy losses and lower frictional losses. The electronic commutation system allows for precise control of the motor’s operation, maximizing efficiency and reducing power consumption.
4. Maintenance:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors require regular maintenance due to the wear and tear of the brushes and commutator. The brushes need periodic replacement, and the commutator requires cleaning to maintain proper electrical contact. The maintenance requirements contribute to additional costs and downtime for brushed DC motors.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors have a relatively maintenance-free operation. As they do not have brushes or commutators, there is no need for brush replacement or commutator cleaning. This results in reduced maintenance costs and increased reliability of brushless DC motors.
5. Speed Control:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors offer simpler speed control options. The speed can be controlled by adjusting the applied voltage or by varying the resistance in the armature circuit. This allows for relatively straightforward speed regulation.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors provide more advanced and precise speed control capabilities. The speed can be controlled through the electronic commutation system by adjusting the timing and sequence of the stator windings’ energization. This allows for precise control of the motor’s speed and acceleration.
These key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors make each type suitable for different applications depending on factors such as efficiency requirements, maintenance considerations, and control complexity.

How do DC motors compare to AC motors in terms of performance and efficiency?
When comparing DC (Direct Current) motors and AC (Alternating Current) motors, several factors come into play, including performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors and AC motors compare in terms of performance and efficiency:
1. Performance:
Speed Control: DC motors typically offer better speed control compared to AC motors. DC motors can be easily controlled by varying the voltage applied to the armature, allowing for precise and smooth speed regulation. On the other hand, AC motors rely on complex control methods such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) to achieve speed control, which can be more challenging and costly.
Starting Torque: DC motors generally provide higher starting torque compared to AC motors. The presence of a separate field winding in DC motors allows for independent control of the field current, enabling higher torque during motor startup. AC motors, especially induction motors, typically have lower starting torque, requiring additional starting mechanisms or devices.
Reversibility: DC motors offer inherent reversibility, meaning they can easily change their rotational direction by reversing the polarity of the applied voltage. AC motors, particularly induction motors, require more complex control mechanisms to achieve reversible operation.
Dynamic Response: DC motors have faster dynamic response characteristics compared to AC motors. They can quickly accelerate or decelerate, making them suitable for applications that require rapid changes in speed or precise control, such as robotics or servo systems.
2. Efficiency:
Full Load Efficiency: AC motors, especially three-phase induction motors, generally exhibit higher full load efficiencies compared to DC motors. This efficiency advantage is primarily due to the absence of commutation and the use of a rotating magnetic field in AC motors, which results in reduced energy losses and improved efficiency.
Partial Load Efficiency: DC motors can have higher efficiency at partial loads compared to AC motors. DC motors can be controlled by adjusting the armature voltage, allowing them to operate at reduced power while maintaining relatively high efficiency. AC motors, especially induction motors, may experience reduced efficiency at partial loads due to factors such as increased iron losses and reduced power factor.
Regenerative Braking: DC motors offer the advantage of regenerative braking, where the motor acts as a generator and converts kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration or braking. This regenerative braking capability allows for energy recovery, increasing overall system efficiency. AC motors typically require additional components or systems to achieve regenerative braking.
Power Factor: AC motors, when properly designed and operated, can have a power factor close to unity. This means that they draw relatively low reactive power from the electrical grid, resulting in improved power system efficiency. DC motors, on the other hand, may exhibit a lower power factor and require power factor correction measures if necessary.
In summary, DC motors and AC motors have their respective strengths and weaknesses in terms of performance and efficiency. DC motors excel in speed control, starting torque, reversibility, and dynamic response. AC motors, particularly three-phase induction motors, generally offer higher full load efficiency and power factor. However, DC motors can achieve higher efficiency at partial loads and have the advantage of regenerative braking. The choice between DC motors and AC motors depends on the specific application requirements, cost considerations, and the desired balance between performance and efficiency.

Are there innovations or emerging technologies in the field of DC motor design?
Yes, there have been several innovations and emerging technologies in the field of DC (Direct Current) motor design. These advancements aim to improve the performance, efficiency, reliability, and overall capabilities of DC motors. Here’s a detailed explanation of some notable innovations and emerging technologies in DC motor design:
1. Brushless DC Motors:
One significant advancement in DC motor design is the development and widespread adoption of brushless DC motors (BLDC motors). Unlike traditional DC motors that use brushes for commutation, BLDC motors employ electronic commutation through the use of permanent magnets and motor controller circuits. This eliminates the need for brushes, reducing maintenance requirements and improving overall motor efficiency and lifespan. BLDC motors offer higher torque density, smoother operation, better speed control, and improved energy efficiency compared to conventional brushed DC motors.
2. High-Efficiency Materials:
The use of high-efficiency materials in DC motor design has been an area of focus for improving motor performance. Advanced magnetic materials, such as neodymium magnets, have allowed for stronger and more compact motor designs. These materials increase the motor’s power density, enabling higher torque output and improved efficiency. Additionally, advancements in materials used for motor windings and core laminations have reduced electrical losses and improved overall motor efficiency.
3. Power Electronics and Motor Controllers:
Advancements in power electronics and motor control technologies have greatly influenced DC motor design. The development of sophisticated motor controllers and efficient power electronic devices enables precise control of motor speed, torque, and direction. These technologies have resulted in more efficient and reliable motor operation, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced motor performance in various applications.
4. Integrated Motor Systems:
Integrated motor systems combine the motor, motor controller, and associated electronics into a single unit. These integrated systems offer compact designs, simplified installation, and improved overall performance. By integrating the motor and controller, issues related to compatibility and communication between separate components are minimized. Integrated motor systems are commonly used in applications such as robotics, electric vehicles, and industrial automation.
5. IoT and Connectivity:
The integration of DC motors with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and connectivity has opened up new possibilities for monitoring, control, and optimization of motor performance. By incorporating sensors, actuators, and connectivity features, DC motors can be remotely monitored, diagnosed, and controlled. This enables predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and real-time performance adjustments, leading to improved efficiency and reliability in various applications.
6. Advanced Motor Control Algorithms:
Advanced motor control algorithms, such as sensorless control and field-oriented control (FOC), have contributed to improved performance and efficiency of DC motors. Sensorless control techniques eliminate the need for additional sensors by leveraging motor current and voltage measurements to estimate rotor position. FOC algorithms optimize motor control by aligning the magnetic field with the rotor position, resulting in improved torque and efficiency, especially at low speeds.
These innovations and emerging technologies in DC motor design have revolutionized the capabilities and performance of DC motors. Brushless DC motors, high-efficiency materials, advanced motor control techniques, integrated motor systems, IoT connectivity, and advanced control algorithms have collectively contributed to more efficient, reliable, and versatile DC motor solutions across various industries and applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-09
China Professional Electric AC DC Servo Motor Drive& Motor for Crimping Curving Machine vacuum pump engine
Product Description
Product Description
1. Small size, saving installation space
2. Strong overload capacity and high operating efficiency
3. Small speed fluctuation and smooth operation
4. Low temperature rise, low noise, high applicability
5. The energy saving is raised to level 1
6. The protection level is increased to IP67
Product Specification
Product Parameters
| Model type | ZE251558D1370L3 | |
| Product Code(mm) | ZE25 | |
| Rated voltage (V) | 380 | |
| Rated power (KW) | 58.1 | |
| Rated torque (N.m) | 370 | |
| Max torque (N.m) | 605 | |
| Rated current (Arms) | 110 | |
| Max current (Arms) | 200 | |
| Rated speed (r/min) | 1500 | |
| Max speed (r/min) | 2200 | |
| Frequency(HZ) | 100 | |
| Counter Electromotive Force(V) | 312 | |
| Rotor Inertia(kg*cm2) | 630 | |
| Line Resistance(Ω) | 0. 0571 | |
| Line Inductance Ld(mH) | 1.32 | |
| Line Inductance Lq(mH) | 2.65 | |
Product Drawing
Detailed Photos
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
Chnchi HangZhou Electric Co.Ltd was established in 2007,covers an area of about 42000 squaremeters, is located in HangZhou where is known as the ancient Chinese capital. The company focuses on industrial electrical equipment of transmission control and energy saving technology, newenergy generation equipment and control technology. The company is private high-tech enter-prises, and its business includes R & D, production,sales and service. We have industrial automation control technology with independent intellectual property rights, provide customers with personalized solutions as quickly as possible, and achieve the common growth of corporate value and customer value as much as possible.
Payment Methods
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
| Samples: |
US$ 2430/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can you explain the basic working principle behind a DC motor?
A DC (Direct Current) motor operates based on the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction. It converts electrical energy into mechanical motion by utilizing the interaction between magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the basic working principle behind a DC motor:
1. Construction:
A DC motor consists of several key components:
- Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the motor and typically consists of permanent magnets or electromagnets that produce a fixed magnetic field.
- Rotor: The rotor is the moving part of the motor and is connected to the shaft. It contains coils or windings that carry the armature current.
- Armature: The armature is the core of the rotor that holds the armature windings. The windings are usually made of copper wire and are evenly spaced around the armature.
- Commutator: The commutator is a cylindrical ring attached to the rotor shaft. It consists of multiple segments, usually made of copper, that are insulated from each other.
- Brushes: The brushes are stationary contacts that make physical contact with the commutator segments. They are typically made of carbon or graphite and provide electrical connections to the armature windings.
2. Electromagnetic Induction:
When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force due to the interaction between the magnetic field and the current. This phenomenon is described by the right-hand rule, where the direction of the force is perpendicular to both the current direction and the magnetic field direction.
3. Motor Operation:
When a DC motor is powered, a DC voltage is applied to the armature windings through the brushes and commutator. The current flowing through the armature windings creates a magnetic field around the windings. This magnetic field interacts with the fixed magnetic field produced by the stator, resulting in a force that causes the rotor to rotate.
4. Commutation:
The commutation process is crucial for the continuous rotation of the rotor in a DC motor. As the rotor spins, the brushes make contact with different commutator segments, effectively reversing the direction of the current in the armature windings at the appropriate timing. This reversal of current flow ensures that the torque generated in the armature windings is always in the same direction, allowing for continuous rotation of the rotor.
5. Speed Control:
The speed of a DC motor can be controlled by varying the applied voltage. Reducing the voltage results in a decrease in the magnetic field strength, which in turn decreases the force acting on the armature windings. This reduction in force leads to a decrease in the motor’s speed. Conversely, increasing the voltage increases the speed of the motor. Precise speed control can be achieved by using electronic circuits to regulate the voltage supplied to the motor.
6. Advantages and Applications:
DC motors offer several advantages, including:
- High starting torque, making them suitable for applications requiring high initial force.
- Excellent speed control capabilities, allowing for precise and adjustable speed regulation.
- Relatively simple construction and ease of maintenance.
- Wide range of sizes and power ratings, making them adaptable to various applications.
DC motors find extensive use in numerous applications, such as robotics, industrial automation, electric vehicles, appliances, and more.
By understanding the basic working principle behind a DC motor, one can appreciate its functionality and explore its applications in different fields.

How do DC motors compare to AC motors in terms of performance and efficiency?
When comparing DC (Direct Current) motors and AC (Alternating Current) motors, several factors come into play, including performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors and AC motors compare in terms of performance and efficiency:
1. Performance:
Speed Control: DC motors typically offer better speed control compared to AC motors. DC motors can be easily controlled by varying the voltage applied to the armature, allowing for precise and smooth speed regulation. On the other hand, AC motors rely on complex control methods such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) to achieve speed control, which can be more challenging and costly.
Starting Torque: DC motors generally provide higher starting torque compared to AC motors. The presence of a separate field winding in DC motors allows for independent control of the field current, enabling higher torque during motor startup. AC motors, especially induction motors, typically have lower starting torque, requiring additional starting mechanisms or devices.
Reversibility: DC motors offer inherent reversibility, meaning they can easily change their rotational direction by reversing the polarity of the applied voltage. AC motors, particularly induction motors, require more complex control mechanisms to achieve reversible operation.
Dynamic Response: DC motors have faster dynamic response characteristics compared to AC motors. They can quickly accelerate or decelerate, making them suitable for applications that require rapid changes in speed or precise control, such as robotics or servo systems.
2. Efficiency:
Full Load Efficiency: AC motors, especially three-phase induction motors, generally exhibit higher full load efficiencies compared to DC motors. This efficiency advantage is primarily due to the absence of commutation and the use of a rotating magnetic field in AC motors, which results in reduced energy losses and improved efficiency.
Partial Load Efficiency: DC motors can have higher efficiency at partial loads compared to AC motors. DC motors can be controlled by adjusting the armature voltage, allowing them to operate at reduced power while maintaining relatively high efficiency. AC motors, especially induction motors, may experience reduced efficiency at partial loads due to factors such as increased iron losses and reduced power factor.
Regenerative Braking: DC motors offer the advantage of regenerative braking, where the motor acts as a generator and converts kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration or braking. This regenerative braking capability allows for energy recovery, increasing overall system efficiency. AC motors typically require additional components or systems to achieve regenerative braking.
Power Factor: AC motors, when properly designed and operated, can have a power factor close to unity. This means that they draw relatively low reactive power from the electrical grid, resulting in improved power system efficiency. DC motors, on the other hand, may exhibit a lower power factor and require power factor correction measures if necessary.
In summary, DC motors and AC motors have their respective strengths and weaknesses in terms of performance and efficiency. DC motors excel in speed control, starting torque, reversibility, and dynamic response. AC motors, particularly three-phase induction motors, generally offer higher full load efficiency and power factor. However, DC motors can achieve higher efficiency at partial loads and have the advantage of regenerative braking. The choice between DC motors and AC motors depends on the specific application requirements, cost considerations, and the desired balance between performance and efficiency.

How does the size and power rating of a DC motor affect its suitability for different tasks?
The size and power rating of a DC (Direct Current) motor play crucial roles in determining its suitability for different tasks and applications. The size and power rating directly impact the motor’s performance characteristics, including its torque output, speed range, efficiency, and overall capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the size and power rating of a DC motor affect its suitability for different tasks:
Size of DC Motor:
The size of a DC motor refers to its physical dimensions, including its diameter, length, and overall volume. The size of the motor influences its ability to fit into specific spaces or applications with space constraints. Here are some key considerations regarding the size of a DC motor:
1. Space Limitations: In applications where space is limited, such as small robotic systems or compact machinery, smaller-sized DC motors are preferred. These motors provide a more convenient and efficient integration into the overall system design.
2. Weight Constraints: Certain applications, such as drones or lightweight robots, may have strict weight limitations. Smaller-sized DC motors are generally lighter, making them more suitable for weight-sensitive tasks where minimizing the overall system weight is essential.
3. Cooling and Heat Dissipation: The size of a DC motor can impact its ability to dissipate heat generated during operation. Smaller-sized motors may have less surface area for heat dissipation, which can lead to increased operating temperatures. In contrast, larger-sized motors typically have better heat dissipation capabilities, allowing for sustained operation under heavy loads or in high-temperature environments.
Power Rating of DC Motor:
The power rating of a DC motor refers to the maximum power it can deliver or the power it consumes during operation. The power rating determines the motor’s capacity to perform work and influences its performance characteristics. Here are some key considerations regarding the power rating of a DC motor:
1. Torque Output: The power rating of a DC motor is directly related to its torque output. Higher power-rated motors generally provide higher torque, allowing them to handle more demanding tasks or applications that require greater force or load capacity. For example, heavy-duty industrial machinery or electric vehicles often require DC motors with higher power ratings to generate sufficient torque for their intended tasks.
2. Speed Range: The power rating of a DC motor affects its speed range capabilities. Motors with higher power ratings can typically achieve higher speeds, making them suitable for applications that require rapid or high-speed operation. On the other hand, lower power-rated motors may have limited speed ranges, making them more suitable for applications that require slower or controlled movements.
3. Efficiency: The power rating of a DC motor can impact its efficiency. Higher power-rated motors tend to have better efficiency, meaning they can convert a larger proportion of electrical input power into mechanical output power. Increased efficiency is desirable in applications where energy efficiency or battery life is a critical factor, such as electric vehicles or portable devices.
4. Overload Capability: The power rating of a DC motor determines its ability to handle overloads or sudden changes in load conditions. Motors with higher power ratings generally have a greater overload capacity, allowing them to handle temporary load spikes without stalling or overheating. This characteristic is crucial in applications where intermittent or varying loads are common.
Overall, the size and power rating of a DC motor are important factors in determining its suitability for different tasks. Smaller-sized motors are advantageous in space-constrained or weight-sensitive applications, while larger-sized motors offer better heat dissipation and can handle heavier loads. Higher power-rated motors provide greater torque, speed range, efficiency, and overload capability, making them suitable for more demanding tasks. It is crucial to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application and choose a DC motor size and power rating that aligns with those requirements to ensure optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-05-07
China Hot selling DC Motors 24V 3000rpm 400watt Hollow Shaft DC Servo Motor for Robot vacuum pump connector
Product Description
Quick Details
Place of Origin:ZheJiang , China (Mainland)
Model Number:KY80AS5714-30
Usage:Boat, Car, AGV,Rail car,Tracked car
Certification:CE
Type:Servo MotorTorque:1.27 Nm
Construction:Permanent Magnet
Commutation:Brushless
Protect Feature:Waterproof
Speed(RPM):3000rpm
Continuous Current(A):18.8A
Output Power:400w
Voltage(V):24v
Efficiency:IE 3
Model:KY80AS5714-30
Product Name:BLDC servo motor
Motor Type:Brushless dc motor
Keywords:BLDC motor
Color:Black
Diameter:80mm
Encoder:YES
Weight:2.2kg
Warranty:1 Year
Application:AGV,Tracked car,Rail car,Serv
Features:
1.Protection grade:IP65, insulation grade:F
2.Winding overhang structure optimization, to minimize the copper loss and iron loss minimization, small volume, light weight, low temperature rise, high efficiency
3.Super high coercivity, the maximum magnetic energy product NdFe35 permanent magnetic materials, strong resistance to demagnetization, motor performance is stable.
4.Low noise, low vibration, low moment of inertia.
5.High torque, fast dynamic response, wide speed range, strong overload capacity (four times)
Product parameters:
| Volt | 24v | Power | 400w |
|
Rated Torque |
1.27Nm |
Rated Speed |
3000rpm |
|
Rated Current |
18.8A |
Peak Torque |
3.8Nm |
|
Line Resistance |
0.05Ω |
Rotor Constan |
0.56mH |
|
Torque constant |
0.06Nm/A |
Back EMF Constant |
10v/kr/min |
|
Rotor Inertia |
281Kg.m2×10-6 |
Mechanical Time Constant |
0.6ms |
|
Electrical Time Constant |
0.5ms |
Encoder |
2500ppr |
| Weight | 2.2kg | Diameter | 80mm |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 10 |
| Samples: |
US$ 129/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
Brushed and brushless DC motors are two distinct types of motors that differ in their construction, operation, and performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors:
1. Construction:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors have a relatively simple construction. They consist of a rotor with armature windings and a commutator, and a stator with permanent magnets or electromagnets. The commutator and brushes make physical contact to provide electrical connections to the armature windings.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors have a more complex construction. They typically consist of a stationary stator with permanent magnets or electromagnets and a rotor with multiple coils or windings. The rotor does not have a commutator or brushes.
2. Commutation:
Brushed DC Motors: In brushed DC motors, the commutator and brushes are responsible for the commutation process. The brushes make contact with different segments of the commutator, reversing the direction of the current through the armature windings as the rotor rotates. This switching of the current direction generates the necessary torque for motor rotation.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors use electronic commutation instead of mechanical commutation. The commutation process is managed by an external electronic controller or driver. The controller determines the timing and sequence of energizing the stator windings based on the rotor position, allowing for precise control of motor operation.
3. Efficiency:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors tend to have lower efficiency compared to brushless DC motors. This is primarily due to the energy losses associated with the brushes and commutation process. The friction and wear between the brushes and commutator result in additional power dissipation and reduce overall motor efficiency.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors are known for their higher efficiency. Since they eliminate the use of brushes and commutators, there are fewer energy losses and lower frictional losses. The electronic commutation system allows for precise control of the motor’s operation, maximizing efficiency and reducing power consumption.
4. Maintenance:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors require regular maintenance due to the wear and tear of the brushes and commutator. The brushes need periodic replacement, and the commutator requires cleaning to maintain proper electrical contact. The maintenance requirements contribute to additional costs and downtime for brushed DC motors.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors have a relatively maintenance-free operation. As they do not have brushes or commutators, there is no need for brush replacement or commutator cleaning. This results in reduced maintenance costs and increased reliability of brushless DC motors.
5. Speed Control:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors offer simpler speed control options. The speed can be controlled by adjusting the applied voltage or by varying the resistance in the armature circuit. This allows for relatively straightforward speed regulation.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors provide more advanced and precise speed control capabilities. The speed can be controlled through the electronic commutation system by adjusting the timing and sequence of the stator windings’ energization. This allows for precise control of the motor’s speed and acceleration.
These key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors make each type suitable for different applications depending on factors such as efficiency requirements, maintenance considerations, and control complexity.

How do DC motors compare to AC motors in terms of performance and efficiency?
When comparing DC (Direct Current) motors and AC (Alternating Current) motors, several factors come into play, including performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors and AC motors compare in terms of performance and efficiency:
1. Performance:
Speed Control: DC motors typically offer better speed control compared to AC motors. DC motors can be easily controlled by varying the voltage applied to the armature, allowing for precise and smooth speed regulation. On the other hand, AC motors rely on complex control methods such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) to achieve speed control, which can be more challenging and costly.
Starting Torque: DC motors generally provide higher starting torque compared to AC motors. The presence of a separate field winding in DC motors allows for independent control of the field current, enabling higher torque during motor startup. AC motors, especially induction motors, typically have lower starting torque, requiring additional starting mechanisms or devices.
Reversibility: DC motors offer inherent reversibility, meaning they can easily change their rotational direction by reversing the polarity of the applied voltage. AC motors, particularly induction motors, require more complex control mechanisms to achieve reversible operation.
Dynamic Response: DC motors have faster dynamic response characteristics compared to AC motors. They can quickly accelerate or decelerate, making them suitable for applications that require rapid changes in speed or precise control, such as robotics or servo systems.
2. Efficiency:
Full Load Efficiency: AC motors, especially three-phase induction motors, generally exhibit higher full load efficiencies compared to DC motors. This efficiency advantage is primarily due to the absence of commutation and the use of a rotating magnetic field in AC motors, which results in reduced energy losses and improved efficiency.
Partial Load Efficiency: DC motors can have higher efficiency at partial loads compared to AC motors. DC motors can be controlled by adjusting the armature voltage, allowing them to operate at reduced power while maintaining relatively high efficiency. AC motors, especially induction motors, may experience reduced efficiency at partial loads due to factors such as increased iron losses and reduced power factor.
Regenerative Braking: DC motors offer the advantage of regenerative braking, where the motor acts as a generator and converts kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration or braking. This regenerative braking capability allows for energy recovery, increasing overall system efficiency. AC motors typically require additional components or systems to achieve regenerative braking.
Power Factor: AC motors, when properly designed and operated, can have a power factor close to unity. This means that they draw relatively low reactive power from the electrical grid, resulting in improved power system efficiency. DC motors, on the other hand, may exhibit a lower power factor and require power factor correction measures if necessary.
In summary, DC motors and AC motors have their respective strengths and weaknesses in terms of performance and efficiency. DC motors excel in speed control, starting torque, reversibility, and dynamic response. AC motors, particularly three-phase induction motors, generally offer higher full load efficiency and power factor. However, DC motors can achieve higher efficiency at partial loads and have the advantage of regenerative braking. The choice between DC motors and AC motors depends on the specific application requirements, cost considerations, and the desired balance between performance and efficiency.

Can DC motors be used in robotics, and if so, what are some notable applications?
Yes, DC (Direct Current) motors can be used in robotics, and they are widely employed in various robotic applications. DC motors offer several advantages that make them suitable for robotic systems, including their controllability, compact size, and versatility. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors are used in robotics and some notable applications:
DC Motors in Robotics:
DC motors are commonly used in robotics due to their ability to provide precise speed control and torque output. They can be easily controlled by adjusting the voltage applied to the motor, allowing for accurate and responsive motion control in robotic systems. Additionally, DC motors can be designed in compact sizes, making them suitable for applications with limited space and weight constraints.
There are two main types of DC motors used in robotics:
- DC Brushed Motors: These motors have a commutator and carbon brushes that provide the electrical connection to the rotating armature. They are relatively simple in design and cost-effective. However, they may require maintenance due to brush wear.
- DC Brushless Motors: These motors use electronic commutation instead of brushes, resulting in improved reliability and reduced maintenance requirements. They are often more efficient and offer higher power density compared to brushed motors.
Notable Applications of DC Motors in Robotics:
DC motors find applications in various robotic systems across different industries. Here are some notable examples:
1. Robotic Manipulators: DC motors are commonly used in robotic arms and manipulators to control the movement of joints and end-effectors. They provide precise control over position, speed, and torque, allowing robots to perform tasks such as pick-and-place operations, assembly, and material handling in industrial automation, manufacturing, and logistics.
2. Mobile Robots: DC motors are extensively utilized in mobile robots, including autonomous vehicles, drones, and rovers. They power the wheels or propellers, enabling the robot to navigate and move in different environments. DC motors with high torque output are particularly useful for off-road or rugged terrain applications.
3. Humanoid Robots: DC motors play a critical role in humanoid robots, which aim to replicate human-like movements and capabilities. They are employed in various joints, including those of the head, arms, legs, and hands, allowing humanoid robots to perform complex movements and tasks such as walking, grasping objects, and facial expressions.
4. Robotic Exoskeletons: DC motors are used in robotic exoskeletons, which are wearable devices designed to enhance human strength and mobility. They provide the necessary actuation and power for assisting or augmenting human movements, such as walking, lifting heavy objects, and rehabilitation purposes.
5. Educational Robotics: DC motors are popular in educational robotics platforms and kits, including those used in schools, universities, and hobbyist projects. They provide a cost-effective and accessible way for students and enthusiasts to learn about robotics, programming, and control systems.
6. Precision Robotics: DC motors with high-precision control are employed in applications that require precise positioning and motion control, such as robotic surgery systems, laboratory automation, and 3D printing. The ability of DC motors to achieve accurate and repeatable movements makes them suitable for tasks that demand high levels of precision.
These are just a few examples of how DC motors are used in robotics. The flexibility, controllability, and compactness of DC motors make them a popular choice in a wide range of robotic applications, contributing to the advancement of automation, exploration, healthcare, and other industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
China best 48V 1000W DC Servo Motor with Encoder, Agv Motor. Robot Motor vacuum pump oil
Product Description
48V 1KW Brushless DC Servo Motor,AGV Motor
Product Features
Protection grade:IP65, insulation grade:F
Winding overhang structure optimization, to minimize the copper loss and iron loss minimization, small volume, light weight, low temperature rise, high efficiency
Super high coercivity, the maximum magnetic energy product NdFe35 permanent magnetic materials, strong resistance to demagnetization, motor performance is stable.
Low noise, low vibration, low moment of inertia.
High torque, fast dynamic response, wide speed range, strong overload capacity (four times)
Features:
*High Torque to inertia ratio&up to 25000Nm/kgm²
*Fast dynamic response *time constant <20ms
*Wide speed adjusting&feedback up to 1000:1
*Steady speed precision up to 0.5%
*High overload,2Mn/30s,3.5N.m/10s
*Small volume and light
*Silent,the lowest noise is only 45dB(A)
*Protected with IP65,Class F insulation
Industry class
1.The altitude should be over 1000 CHINAMFG above sea level
2.Environment temperature:+5ºC~+40ºC
3.The month average tallest relative humidity is 90%,at the same the month average lowest
temperature is less than 25
| Model | KY110AS571-15 |
| VOLT | 48VDC |
| POWER | 1000W |
| SPEED | 1500RPM |
| TORQUE | 6.3N.M |
| ENCODER | 2500PPR |
| APPLICATION | AGV ROBOT,FIRE ROBOT,ELECTRIC VEHICLE |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 10 |
| Samples: |
US$ 235/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
Brushed and brushless DC motors are two distinct types of motors that differ in their construction, operation, and performance characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors:
1. Construction:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors have a relatively simple construction. They consist of a rotor with armature windings and a commutator, and a stator with permanent magnets or electromagnets. The commutator and brushes make physical contact to provide electrical connections to the armature windings.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors have a more complex construction. They typically consist of a stationary stator with permanent magnets or electromagnets and a rotor with multiple coils or windings. The rotor does not have a commutator or brushes.
2. Commutation:
Brushed DC Motors: In brushed DC motors, the commutator and brushes are responsible for the commutation process. The brushes make contact with different segments of the commutator, reversing the direction of the current through the armature windings as the rotor rotates. This switching of the current direction generates the necessary torque for motor rotation.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors use electronic commutation instead of mechanical commutation. The commutation process is managed by an external electronic controller or driver. The controller determines the timing and sequence of energizing the stator windings based on the rotor position, allowing for precise control of motor operation.
3. Efficiency:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors tend to have lower efficiency compared to brushless DC motors. This is primarily due to the energy losses associated with the brushes and commutation process. The friction and wear between the brushes and commutator result in additional power dissipation and reduce overall motor efficiency.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors are known for their higher efficiency. Since they eliminate the use of brushes and commutators, there are fewer energy losses and lower frictional losses. The electronic commutation system allows for precise control of the motor’s operation, maximizing efficiency and reducing power consumption.
4. Maintenance:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors require regular maintenance due to the wear and tear of the brushes and commutator. The brushes need periodic replacement, and the commutator requires cleaning to maintain proper electrical contact. The maintenance requirements contribute to additional costs and downtime for brushed DC motors.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors have a relatively maintenance-free operation. As they do not have brushes or commutators, there is no need for brush replacement or commutator cleaning. This results in reduced maintenance costs and increased reliability of brushless DC motors.
5. Speed Control:
Brushed DC Motors: Brushed DC motors offer simpler speed control options. The speed can be controlled by adjusting the applied voltage or by varying the resistance in the armature circuit. This allows for relatively straightforward speed regulation.
Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors provide more advanced and precise speed control capabilities. The speed can be controlled through the electronic commutation system by adjusting the timing and sequence of the stator windings’ energization. This allows for precise control of the motor’s speed and acceleration.
These key differences between brushed and brushless DC motors make each type suitable for different applications depending on factors such as efficiency requirements, maintenance considerations, and control complexity.

What role does commutation play in the operation of a DC motor?
In the operation of a DC (Direct Current) motor, commutation plays a crucial role in ensuring the continuous rotation of the motor and the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical motion. It is the process by which the direction of the current in the armature winding is periodically reversed to maintain a constant torque and facilitate the rotation of the motor. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role of commutation in the operation of a DC motor:
Commutation is necessary in a DC motor because the magnetic field generated by the armature winding needs to be constantly aligned with the stator’s magnetic field for efficient torque production. The stator of a DC motor typically consists of permanent magnets or electromagnets that create a fixed magnetic field. The armature winding, located on the rotor, produces a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s field to generate torque.
The commutation process is achieved through the use of a commutator and brushes. The commutator is a cylindrical ring with multiple segments, while the brushes are conductive contacts that make physical contact with the commutator segments. The armature winding is connected to the commutator, and as the rotor spins, the brushes maintain contact with different segments.
As the rotor rotates, the commutator and brushes ensure that the direction of the current in the armature winding is reversed at specific intervals. This reversal of current flow is necessary to maintain a consistent torque in the same rotational direction. Without commutation, the torque generated by the motor would fluctuate in both magnitude and direction, leading to instability and erratic motor behavior.
The commutation process involves two stages: mechanical commutation and electrical commutation.
1. Mechanical Commutation: As the rotor rotates, the brushes make contact with different segments of the commutator. The segments are insulated from each other to prevent short circuits. When the brushes move from one segment to another, the current flowing through the armature winding is switched to a different coil or set of coils. This mechanical switching ensures that the magnetic fields produced by the winding are properly aligned with the stator’s field, resulting in continuous torque production.
2. Electrical Commutation: The reversal of current in the armature winding is achieved through electrical commutation. When the brushes make contact with a new commutator segment, the current flow in the winding is redirected to maintain the desired torque direction. The timing and sequence of the current reversal are critical to ensure smooth and efficient motor operation.
The commutation process in a DC motor is a dynamic and continuous operation. It allows for the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical motion by providing a consistent torque output. The efficiency and performance of the motor are greatly influenced by the quality and effectiveness of the commutation process.
In summary, commutation plays a vital role in the operation of a DC motor by ensuring the continuous rotation of the motor and the production of consistent torque. It involves the mechanical and electrical switching of the current direction in the armature winding, facilitated by the commutator and brushes.

Can DC motors be used in robotics, and if so, what are some notable applications?
Yes, DC (Direct Current) motors can be used in robotics, and they are widely employed in various robotic applications. DC motors offer several advantages that make them suitable for robotic systems, including their controllability, compact size, and versatility. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors are used in robotics and some notable applications:
DC Motors in Robotics:
DC motors are commonly used in robotics due to their ability to provide precise speed control and torque output. They can be easily controlled by adjusting the voltage applied to the motor, allowing for accurate and responsive motion control in robotic systems. Additionally, DC motors can be designed in compact sizes, making them suitable for applications with limited space and weight constraints.
There are two main types of DC motors used in robotics:
- DC Brushed Motors: These motors have a commutator and carbon brushes that provide the electrical connection to the rotating armature. They are relatively simple in design and cost-effective. However, they may require maintenance due to brush wear.
- DC Brushless Motors: These motors use electronic commutation instead of brushes, resulting in improved reliability and reduced maintenance requirements. They are often more efficient and offer higher power density compared to brushed motors.
Notable Applications of DC Motors in Robotics:
DC motors find applications in various robotic systems across different industries. Here are some notable examples:
1. Robotic Manipulators: DC motors are commonly used in robotic arms and manipulators to control the movement of joints and end-effectors. They provide precise control over position, speed, and torque, allowing robots to perform tasks such as pick-and-place operations, assembly, and material handling in industrial automation, manufacturing, and logistics.
2. Mobile Robots: DC motors are extensively utilized in mobile robots, including autonomous vehicles, drones, and rovers. They power the wheels or propellers, enabling the robot to navigate and move in different environments. DC motors with high torque output are particularly useful for off-road or rugged terrain applications.
3. Humanoid Robots: DC motors play a critical role in humanoid robots, which aim to replicate human-like movements and capabilities. They are employed in various joints, including those of the head, arms, legs, and hands, allowing humanoid robots to perform complex movements and tasks such as walking, grasping objects, and facial expressions.
4. Robotic Exoskeletons: DC motors are used in robotic exoskeletons, which are wearable devices designed to enhance human strength and mobility. They provide the necessary actuation and power for assisting or augmenting human movements, such as walking, lifting heavy objects, and rehabilitation purposes.
5. Educational Robotics: DC motors are popular in educational robotics platforms and kits, including those used in schools, universities, and hobbyist projects. They provide a cost-effective and accessible way for students and enthusiasts to learn about robotics, programming, and control systems.
6. Precision Robotics: DC motors with high-precision control are employed in applications that require precise positioning and motion control, such as robotic surgery systems, laboratory automation, and 3D printing. The ability of DC motors to achieve accurate and repeatable movements makes them suitable for tasks that demand high levels of precision.
These are just a few examples of how DC motors are used in robotics. The flexibility, controllability, and compactness of DC motors make them a popular choice in a wide range of robotic applications, contributing to the advancement of automation, exploration, healthcare, and other industries.


editor by CX 2024-04-12
China OEM 5812/5816 Electric Electrical Fan AC DC Mini Single Phase Servo Universal Induction Motor for /Refrigerator Fan Motor/Water Pump /Exhausat Fan/Bath Ventilation vacuum pump connector
Product Description
58series shaded Pole Motor
Motor Description:
1.Our motors performance(data) are per customers` requirments.
2.Motor wires are cooper and some could be used aluminium wire to save cost
3.Motors could be used ball bearing and oil bear(Sleeve bearing) both.
4.Insulation Class B/F
withstand voltage:1800V/S/0.5mA
Rotation:CW (view from the shaft side)
Noise<50dB
Interturn Isulation:>2100V
Isulation Resistance:20MΩ
IP:34
Life span:>2000Hours (continuous working).Normal use:10 years
Operation Temperature/Humidity Range:-40°C to +65°C, 0%~95%
5.Safe,reliable, low noise, high performance,characteristics hard, good and stable starting, long life, etc.
6.Typical Application: Exhaust fan, air purifier, micro-oven, fan, induction cooker, refrigerator, pump, heater, hood oven, blwer, air conditioner, Heater machines, dehumidifiers
7.Motor Specification as below chart
| MODEL | A OF SIZE | SHAFT DIA | VOLT | POWER | TORQUE | SPEED RATED |
| YJ5812 | 12MM | 4MM | 110-240V | 10W | 6.71mN.m | 3000RPM |
| YJ5816 | 13MM | 4MM | 110-240V | 13W | 6.85mN.m | 3000RPM |
| YJ5820 | 20MM | 5MM | 110-240V | 15W | 8.89mN.m | 3400RPM |
| YJ5830 | 30MM | 4MM | 110-240V | 50W | 12.9mN.m | 3400RPM |
Fine Watt motor focus on offering motor solutions to smart products for home appliance ,like BLDC,Capacitor motor,shaded pole motor,universal motor and mini generator. Our motors are widely used in kitchen,air conditional,Ice chest,washing machine,etc. Customers locate not only in China domestic ,also oversea from Asia to European and Amecica. Our engineer with 20 years experience in motor design and development,win a lot of motor inovation technology award,Our engineer also provide technical support to other big facotry.we believe we always can find the best solution for your product.
Company FAQ
(1) Q: What kind motors you can provide?
A:For now,we mainly provide Kitchen Hood Motor,DC Motor,Gear Motor,Fan Motor Refrigerator Motor,Hair Dryer Motor Blender Motor Mixer Motor,
BLDC Motor,Shade Pole Motor,Capacitor Motor, PMDC Motor,Synchronous Motor,etc
(2) Q: Is it possible to visit your factory
A: Sure. We always like to meet our customer face to face,this is better for understanding.But please kindly keep us posted a few days in advance so we can make good arrangement.
(3) Q: Can I get some samples
A: It depends. If only a few samples for personal use or replacement, I am afraid it will be difficult for us to provide, because all of our motors are custom made and no stock available if there is no further needs. If just sample testing before the official order and our MOQ, price and other terms are acceptable, we will provide samples.
(4) Q: Is there a MOQ for your motors?
A: Yes. The MOQ is between 1000~10,000pcs for different models after sample approval.
But it’s also okay for us to accept smaller lots like a few dozens, hundreds or thousands
For the initial 3 orders after sample approval.For samples, there is no MOQ requirement. But the less the better (like no more than 5pcs) on condition that the quantity is enough in case any changes needed after initial testing.
(5)Q: What advantage do you have?
A: For motors, we have quality guarantee, if there is probelm motor after inspection in customer house,we will replace .
For service, we offer 24 hours technical support and barrier-free communication with excellent service people.
Technical service: Except offer actual motor products,we can also offer motor technical supporting seperately to our customer.Our engineers are represent the most advanced techonogy.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the main components of a DC motor, and how do they contribute to its functionality?
A DC (Direct Current) motor consists of several key components that work together to enable its functionality. Each component plays a crucial role in the operation of the motor. Here’s a detailed explanation of the main components of a DC motor and their contributions:
1. Stator:
The stator is the stationary part of the motor. It typically consists of permanent magnets or electromagnets that produce a fixed magnetic field. The stator’s magnetic field interacts with the rotor’s magnetic field to generate the required torque for motor rotation. The stator provides the foundation for the motor’s magnetic field and contributes to its overall stability and efficiency.
2. Rotor:
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and is connected to the motor’s output shaft. It contains coils or windings that carry the armature current. The rotor’s windings interact with the stator’s magnetic field, resulting in the generation of a mechanical force that causes the rotor to rotate. The rotor’s movement is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, enabling the motor to perform its intended function.
3. Armature:
The armature is the core of the rotor that holds the armature windings. The armature windings are typically made of copper wire and are evenly spaced around the armature. When a current passes through the armature windings, a magnetic field is created around them. This magnetic field interacts with the stator’s magnetic field, resulting in the generation of a torque that drives the rotor’s rotation. The armature is a critical component that facilitates the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy.
4. Commutator:
The commutator is a cylindrical ring attached to the rotor shaft. It consists of multiple segments, usually made of copper, that are insulated from each other. The commutator plays a vital role in the DC motor’s operation by providing the necessary electrical connections to the armature windings. As the rotor spins, the brushes make physical contact with different commutator segments, effectively reversing the direction of the current in the armature windings at the appropriate timing. This reversal of current flow ensures that the torque generated in the armature windings is always in the same direction, allowing for continuous rotation of the rotor.
5. Brushes:
The brushes are stationary contacts that make physical contact with the commutator segments. They are typically made of carbon or graphite and provide electrical connections to the armature windings. The brushes supply the current to the armature windings through the commutator, allowing for the creation of the magnetic field necessary for motor operation. The brushes need to maintain proper contact with the commutator to ensure efficient electrical transmission and reliable motor performance.
6. Housing or Frame:
The housing or frame of the DC motor encloses and supports all the internal components. It provides structural integrity, protects the motor from external elements, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. The housing or frame also serves as a mounting point for the motor, allowing it to be securely installed in various applications.
By understanding the main components of a DC motor and their contributions, one can gain insights into how each part works together harmoniously to achieve the desired motor functionality.

Can DC motors be used in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines or solar tracking systems?
Yes, DC (Direct Current) motors can be effectively used in various renewable energy systems, including wind turbines and solar tracking systems. The unique characteristics and advantages of DC motors make them well-suited for these applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of how DC motors can be utilized in renewable energy systems:
1. Wind Turbines:
DC motors can be employed in wind turbines to convert the mechanical energy of the wind into electrical energy. There are two common configurations:
a. Direct Drive Wind Turbines:
In direct drive wind turbines, the rotor of the turbine is directly connected to a DC generator. The rotor’s rotational motion is transmitted directly to the generator, which produces DC electrical power. DC motors can be used as DC generators in this configuration. The advantage of using DC motors/generators is their simplicity, reliability, and ability to operate efficiently at variable speeds, which is beneficial in varying wind conditions.
b. Hybrid Wind Turbines:
Hybrid wind turbines combine both aerodynamic and electrical conversion systems. In this configuration, DC motors can be utilized for the pitch control mechanism and yaw control system. The pitch control mechanism adjusts the angle of the turbine blades to optimize performance, while the yaw control system enables the turbine to align itself with the wind direction. DC motors provide precise control and responsiveness required for these functions.
2. Solar Tracking Systems:
DC motors are commonly employed in solar tracking systems to maximize the efficiency of solar panels by optimizing their orientation towards the sun. There are two main types of solar tracking systems:
a. Single-Axis Solar Tracking Systems:
Single-axis solar tracking systems adjust the inclination of solar panels along a single axis (typically the east-west axis) to track the movement of the sun throughout the day. DC motors can be used to drive the rotation mechanism that adjusts the panel’s tilt angle. By continuously adjusting the panel’s position to face the sun directly, the solar energy harvested can be significantly increased, resulting in higher energy output compared to fixed solar panel installations.
b. Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems:
Dual-axis solar tracking systems adjust the inclination of solar panels along both the east-west and north-south axes to track the sun’s movement throughout the day and throughout the year. DC motors are utilized in the rotation mechanisms for both axes. This type of solar tracking system provides the highest possible energy yield by keeping the solar panels perpendicular to the sun’s rays at all times, maximizing the exposure to sunlight.
DC motors are preferred in renewable energy systems due to their advantages, including:
- Efficiency at Variable Speeds: DC motors can operate efficiently at varying speeds, making them suitable for applications with fluctuating wind speeds or changing solar angles.
- Control and Precision: DC motors offer precise control and responsiveness, allowing for accurate tracking and adjustment in wind turbines and solar tracking systems.
- Reliability: DC motors are known for their reliability, with fewer moving parts compared to other motor types, reducing the risk of failure in remote or harsh environments.
- Compatibility with Energy Storage Systems: DC motors can easily be integrated with energy storage systems, such as batteries or supercapacitors, to store excess electrical energy generated by wind turbines or solar panels.
In conclusion, DC motors can be effectively utilized in renewable energy systems such as wind turbines and solar tracking systems. Their efficiency, control capabilities, reliability, and compatibility with energy storage systems make them a suitable choice for these applications, contributing to the advancement of sustainable energy generation.

What are the environmental implications of using DC motors, particularly in green technologies?
DC (Direct Current) motors offer several environmental benefits when used in green technologies. Their characteristics and operational advantages contribute to reducing environmental impact compared to other motor types. Here’s a detailed explanation of the environmental implications of using DC motors, particularly in green technologies:
1. Energy Efficiency:
DC motors are known for their high energy efficiency. Compared to AC (Alternating Current) motors, DC motors generally have lower energy losses and can convert a larger proportion of electrical input power into mechanical output power. This increased efficiency results in reduced energy consumption, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and decreased reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation.
2. Renewable Energy Integration:
DC motors are well-suited for integration with renewable energy sources. Many green technologies, such as solar photovoltaic systems and wind turbines, produce DC power. By utilizing DC motors directly in these systems, the need for power conversion from DC to AC can be minimized, reducing energy losses associated with conversion processes. This integration improves the overall system efficiency and contributes to a more sustainable energy infrastructure.
3. Battery-Powered Applications:
DC motors are commonly used in battery-powered applications, such as electric vehicles and portable devices. The efficiency of DC motors ensures optimal utilization of the limited energy stored in batteries, resulting in extended battery life and reduced energy waste. By utilizing DC motors in these applications, the environmental impact of fossil fuel consumption for transportation and energy storage is reduced.
4. Reduced Emissions:
DC motors, especially brushless DC motors, produce fewer emissions compared to internal combustion engines or motors that rely on fossil fuels. By using DC motors in green technologies, such as electric vehicles or electrically powered equipment, the emission of greenhouse gases and air pollutants associated with traditional combustion engines is significantly reduced. This contributes to improved air quality and a reduction in overall carbon footprint.
5. Noise Reduction:
DC motors generally operate with lower noise levels compared to some other motor types. The absence of brushes in brushless DC motors and the smoother operation of DC motor designs contribute to reduced noise emissions. This is particularly beneficial in green technologies like electric vehicles or renewable energy systems, where quieter operation enhances user comfort and minimizes noise pollution in residential or urban areas.
6. Recycling and End-of-Life Considerations:
DC motors, like many electrical devices, can be recycled at the end of their operational life. The materials used in DC motors, such as copper, aluminum, and various magnets, can be recovered and reused, reducing the demand for new raw materials and minimizing waste. Proper recycling and disposal practices ensure that the environmental impact of DC motors is further mitigated.
The use of DC motors in green technologies offers several environmental benefits, including increased energy efficiency, integration with renewable energy sources, reduced emissions, noise reduction, and the potential for recycling and end-of-life considerations. These characteristics make DC motors a favorable choice for sustainable and environmentally conscious applications, contributing to the transition to a greener and more sustainable future.


editor by CX 2024-03-30
China Stable Speed Control SZGH General servo and spindle motors and spindle servo driver set for textile motor efficiency
Guarantee: 1year
Design Quantity: GH165-140CGD12
Variety: Spindle Servo Motor
Frequency: 50/60Hz
Stage: Three-stage
Shield Attribute: Explosion-proof
AC Voltage: 220 / 380V, 380V
Effectiveness: IE four
Kind:: Spindle servo motor
Design Variety:: SZGH165-140CGD12
Rated Electricity(kW):: 2.2KW
Torque: 14NM
Phase:: A few-period
Rated Existing(A):: 4.9A
Rated Speed(RPM):: 1500-8000rpm
Packaging Details: Common Package deal
Stable Velocity Control CZPT General servo and spindle motors and spindle servo driver established for textile SZGH AC spindle motor can be support .75kw -220kw , RPM -24000rpm Large efficiency Manage perform thorough: steady speed manage, precise place management, exceptional torque handle. Protected & Dependable Merchandise comply with international expectations, through the CE certification. Established up numerous defense circuit, the thorough protection of protection gear.Widely utilized in cnc machine,machine instruments, robot, petroleum, textile, printing, metallurgy, artillery, CNC machining QD sequence black oxided carbon metal SF bushing for bearings radar and other automatic control gear.
| Power | 2.2kw |
| Rated Torque | 14NM |
| Rated speed | 1500rpm |
| Max speed | 8000RPM |
| Mounting | B3( Foot) B5(Body) B35 |
| Matched driver | SZGH-S4T2P2 |
Benefits of a Planetary Motor
If you’re looking for an affordable way to power a machine, consider purchasing a Planetary Motor. These units are designed to provide a massive range of gear reductions, and are capable of generating much higher torques and torque density than other types of drive systems. This article will explain why you should consider purchasing one for your needs. And we’ll also discuss the differences between a planetary and spur gear system, as well as how you can benefit from them.
planetary gears
Planetary gears in a motor are used to reduce the speed of rotation of the armature 8. The reduction ratio is determined by the structure of the planetary gear device. The output shaft 5 rotates through the device with the assistance of the ring gear 4. The ring gear 4 engages with the pinion 3 once the shaft is rotated to the engagement position. The transmission of rotational torque from the ring gear to the armature causes the motor to start.
The axial end surface of a planetary gear device has two circular grooves 21. The depressed portion is used to retain lubricant. This lubricant prevents foreign particles from entering the planetary gear space. This feature enables the planetary gear device to be compact and lightweight. The cylindrical portion also minimizes the mass inertia. In this way, the planetary gear device can be a good choice for a motor with limited space.
Because of their compact footprint, planetary gears are great for reducing heat. In addition, this design allows them to be cooled. If you need high speeds and sustained performance, you may want to consider using lubricants. The lubricants present a cooling effect and reduce noise and vibration. If you want to maximize the efficiency of your motor, invest in a planetary gear hub drivetrain.
The planetary gear head has an internal sun gear that drives the multiple outer gears. These gears mesh together with the outer ring that is fixed to the motor housing. In industrial applications, planetary gears are used with an increasing number of teeth. This distribution of power ensures higher efficiency and transmittable torque. There are many advantages of using a planetary gear motor. These advantages include:
planetary gearboxes
A planetary gearbox is a type of drivetrain in which the input and output shafts are connected with a planetary structure. A planetary gearset can have three main components: an input gear, a planetary output gear, and a stationary position. Different gears can be used to change the transmission ratios. The planetary structure arrangement gives the planetary gearset high rigidity and minimizes backlash. This high rigidity is crucial for quick start-stop cycles and rotational direction.
Planetary gears need to be lubricated regularly to prevent wear and tear. In addition, transmissions must be serviced regularly, which can include fluid changes. The gears in a planetary gearbox will wear out with time, and any problems should be repaired immediately. However, if the gears are damaged, or if they are faulty, a planetary gearbox manufacturer will repair it for free.
A planetary gearbox is typically a 2-speed design, but professional manufacturers can provide triple and single-speed sets. Planetary gearboxes are also compatible with hydraulic, electromagnetic, and dynamic braking systems. The first step to designing a planetary gearbox is defining your application and the desired outcome. Famous constructors use a consultative modeling approach, starting each project by studying machine torque and operating conditions.
As the planetary gearbox is a compact design, space is limited. Therefore, bearings need to be selected carefully. The compact needle roller bearings are the most common option, but they cannot tolerate large axial forces. Those that can handle high axial forces, such as worm gears, should opt for tapered roller bearings. So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of a helical gearbox?
planetary gear motors
When we think of planetary gear motors, we tend to think of large and powerful machines, but in fact, there are many smaller, more inexpensive versions of the same machine. These motors are often made of plastic, and can be as small as six millimeters in diameter. Unlike their larger counterparts, they have only one gear in the transmission, and are made with a small diameter and small number of teeth.
They are similar to the solar system, with the planets rotating around a sun gear. The planet pinions mesh with the ring gear inside the sun gear. All of these gears are connected by a planetary carrier, which is the output shaft of the gearbox. The ring gear and planetary carrier assembly are attached to each other through a series of joints. When power is applied to any of these members, the entire assembly will rotate.
Compared to other configurations, planetary gearmotors are more complicated. Their construction consists of a sun gear centered in the center and several smaller gears that mesh with the central sun gear. These gears are enclosed in a larger internal tooth gear. This design allows them to handle larger loads than conventional gear motors, as the load is distributed among several gears. This type of motor is typically more expensive than other configurations, but can withstand the higher-load requirements of some machines.
Because they are cylindrical in shape, planetary gear motors are incredibly versatile. They can be used in various applications, including automatic transmissions. They are also used in applications where high-precision and speed are necessary. Furthermore, the planetary gear motor is robust and is characterized by low vibrations. The advantages of using a planetary gear motor are vast and include: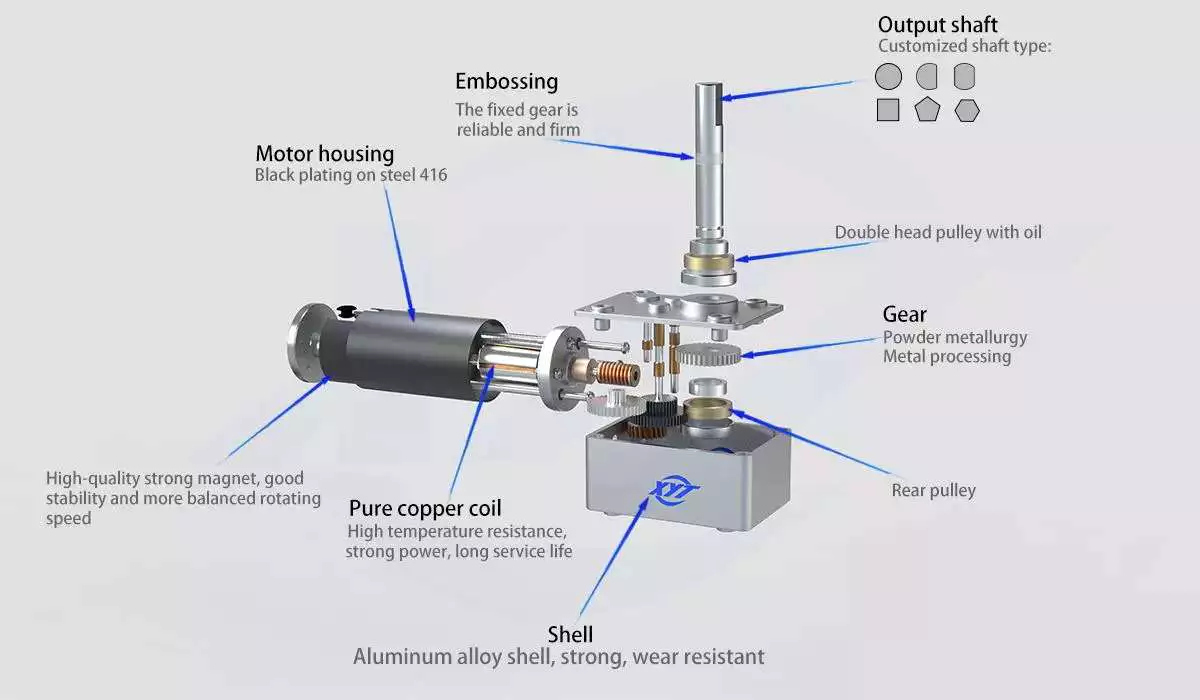
planetary gears vs spur gears
A planetary motor uses multiple teeth to share the load of rotating parts. This gives planetary gears high stiffness and low backlash – often as low as one or two arc minutes. These characteristics are important for applications that undergo frequent start-stop cycles or rotational direction changes. This article discusses the benefits of planetary gears and how they differ from spur gears. You can watch the animation below for a clearer understanding of how they operate and how they differ from spur gears.
Planetary gears move in a periodic manner, with a relatively small meshing frequency. As the meshing frequency increases, the amplitude of the frequency also increases. The amplitude of this frequency is small at low clearance values, and increases dramatically at higher clearance levels. The amplitude of the frequency is higher when the clearance reaches 0.2-0.6. The amplitude increases rapidly, whereas wear increases slowly after the initial 0.2-0.6-inch-wide clearance.
In high-speed, high-torque applications, a planetary motor is more effective. It has multiple contact points for greater torque and higher speed. If you are not sure which type to choose, you can consult with an expert and design a custom gear. If you are unsure of what type of motor you need, contact Twirl Motor and ask for help choosing the right one for your application.
A planetary gear arrangement offers a number of advantages over traditional fixed-axis gear system designs. The compact size allows for lower loss of effectiveness, and the more planets in the gear system enhances the torque density and capacity. Another benefit of a planetary gear system is that it is much stronger and more durable than its spur-gear counterpart. Combined with its many advantages, a planetary gear arrangement offers a superior solution to your shifting needs.
planetary gearboxes as a compact alternative to pinion-and-gear reducers
While traditional pinion-and-gear reducer design is bulky and complex, planetary gearboxes are compact and flexible. They are suitable for many applications, especially where space and weight are issues, as well as torque and speed reduction. However, understanding their mechanism and working isn’t as simple as it sounds, so here are some of the key benefits of planetary gearing.
Planetary gearboxes work by using two planetary gears that rotate around their own axes. The sun gear is used as the input, while the planetary gears are connected via a casing. The ratio of these gears is -Ns/Np, with 24 teeth in the sun gear and -3/2 on the planet gear.
Unlike traditional pinion-and-gear reducer designs, planetary gearboxes are much smaller and less expensive. A planetary gearbox is about 50% smaller and weighs less than a pinion-and-gear reducer. The smaller gear floats on top of three large gears, minimizing the effects of vibration and ensuring consistent transmission over time.
Planetary gearboxes are a good alternative to pinion-and-gear drive systems because they are smaller, less complex and offer a higher reduction ratio. Their meshing arrangement is similar to the Milky Way, with the sun gear in the middle and two or more outer gears. They are connected by a carrier that sets their spacing and incorporates an output shaft.
Compared to pinion-and-gear reduces, planetary gearboxes offer higher speed reduction and torque capacity. As a result, planetary gearboxes are small and compact and are often preferred for space-constrained applications. But what about the high torque transfer? If you’re looking for a compact alt


editor by czh 2023-02-21
China HG-KR13 servo motor motor engine
Guarantee: Other
Model Variety: HG-KR13
Variety: SERVO MOTOR
Frequency: fifty/60Hz
Period: Solitary-phase
AC Voltage: other
Performance: IE 1
Rated Pace: 3000r/min
Rated Electrical power: .1kw
Packaging Specifics: carton box
Specification
| item | value |
| Warranty | Other |
| Place of Origin | ZheJiang |
| Brand Identify | none |
| Model Variety | HG-KR13 |
| Type | SERVO MOTOR |
| Frequency | 50/60Hz |
| Phase | Single-period |
| Efficiency | IE 1 |
| Rated Pace | 3000r/min |
| Rated Electricity | 0.1kw |
ASIC products internal, good trustworthiness, long lifestyle, anti-jamming performance. Stainless metal shaft has a increased security and security.Metal shell is far more reliable and anti-effect. Bearing load weighty, anti-oil and h2o
Servo-motor Encoder GSM48 Collection.Widely employed in the area of automated control AC servo unit, specifically appropriate for use in servo motor supporting.
Internal ASIC products, large reliability, prolonged existence, robust anti-interference. Broad variety of resolutions, and does not call for signal conditioning. With A, B, Z and U, V, W six-channel sign output can be linked with regular line driver (26LS31) RS422, can supply 12 output sign, and is appropriate with TTL
Hollow Shaft Kind GHB38 Collection.Used in automated manage, measurement, robotic X-Y working platform, printing and packaging.Inside ASIC units, substantial dependability, prolonged life, robust anti-interference. far more solid metallic housing could anti-shock. Outlet stop metallic interface sets of water-resistant security.
Hollow Shaft Type GHH80 sequence.Used in computerized management, measurement, robotic X-Y working system, printing and packaging.Inside ASIC products, high dependability, long daily life, sturdy anti-interference. much more reliable metal housing could anti-shock. Outlet conclude metal interface sets of water-resistant protection.
Guide Pulse Generator TM1469 collection.For CNC device origin correction and sign split.
Total plastic housing, large dielectric energy, the axis transfer switch and Oil Pollution Prevention seal layout.
Draw-wire Placement Sensor CESI collection.compact measurement, rugged construction, straightforward to put in
economic expense, and price financial savings for customersVarious alerts output optional: push-pull, TTL, open collector and so on
The cylinders, CN52 Oem Outboard Limited Shaft Foredom Flex Cast Boat And Ship Stern testing equipment and other market has reached big-scale apps, dependability
The Basics of a Planetary Motor
A Planetary Motor is a type of gearmotor that uses multiple planetary gears to deliver torque. This system minimizes the chances of failure of individual gears and increases output capacity. Compared to the planetary motor, the spur gear motor is less complex and less expensive. However, a spur gear motor is generally more suitable for applications requiring low torque. This is because each gear is responsible for the entire load, limiting its torque.
Self-centering planetary gears
This self-centering mechanism for a planetary motor is based on a helical arrangement. The helical structure involves a sun-planet, with its crown and slope modified. The gears are mounted on a ring and share the load evenly. The helical arrangement can be either self-centering or self-resonant. This method is suited for both applications.
A helical planetary gear transmission is illustrated in FIG. 1. A helical configuration includes an output shaft 18 and a sun gear 18. The drive shaft extends through an opening in the cover to engage drive pins on the planet carriers. The drive shaft of the planetary gears can be fixed to the helical arrangement or can be removable. The transmission system is symmetrical, allowing the output shaft of the planetary motor to rotate radially in response to the forces acting on the planet gears.
A flexible pin can improve load sharing. This modification may decrease the face load distribution, but increases the (K_Hbeta) parameter. This effect affects the gear rating and life. It is important to understand the effects of flexible pins. It is worth noting that there are several other disadvantages of flexible pins in helical PGSs. The benefits of flexible pins are discussed below.
Using self-centering planetary gears for a helical planetary motor is essential for symmetrical force distribution. These gears ensure the symmetry of force distribution. They can also be used for self-centering applications. Self-centering planetary gears also guarantee the proper force distribution. They are used to drive a planetary motor. The gearhead is made of a ring gear, and the output shaft is supported by two ball bearings. Self-centering planetary gears can handle a high torque input, and can be suited for many applications.
To solve for a planetary gear mechanism, you need to find its pitch curve. The first step is to find the radius of the internal gear ring. A noncircular planetary gear mechanism should be able to satisfy constraints that can be complex and nonlinear. Using a computer, you can solve for these constraints by analyzing the profile of the planetary wheel’s tooth curve.
High torque
Compared to the conventional planetary motors, high-torque planetary motors have a higher output torque and better transmission efficiency. The high-torque planetary motors are designed to withstand large loads and are used in many types of applications, such as medical equipment and miniature consumer electronics. Their compact design makes them suitable for small space-saving applications. In addition, these motors are designed for high-speed operation.
They come with a variety of shaft configurations and have a wide range of price-performance ratios. The FAULHABER planetary gearboxes are made of plastic, resulting in a good price-performance ratio. In addition, plastic input stage gears are used in applications requiring high torques, and steel input stage gears are available for higher speeds. For difficult operating conditions, modified lubrication is available.
Various planetary gear motors are available in different sizes and power levels. Generally, planetary gear motors are made of steel, brass, or plastic, though some use plastic for their gears. Steel-cut gears are the most durable, and are ideal for applications that require a high amount of torque. Similarly, nickel-steel gears are more lubricated and can withstand a high amount of wear.
The output torque of a high-torque planetary gearbox depends on its rated input speed. Industrial-grade high-torque planetary gearboxes are capable of up to 18000 RPM. Their output torque is not higher than 2000 nm. They are also used in machines where a planet is decelerating. Their working temperature ranges between 25 and 100 degrees Celsius. For best results, it is best to choose the right size for the application.
A high-torque planetary gearbox is the most suitable type of high-torque planetary motor. It is important to determine the deceleration ratio before buying one. If there is no product catalog that matches your servo motor, consider buying a close-fitting high-torque planetary gearbox. There are also high-torque planetary gearboxes available for custom-made applications.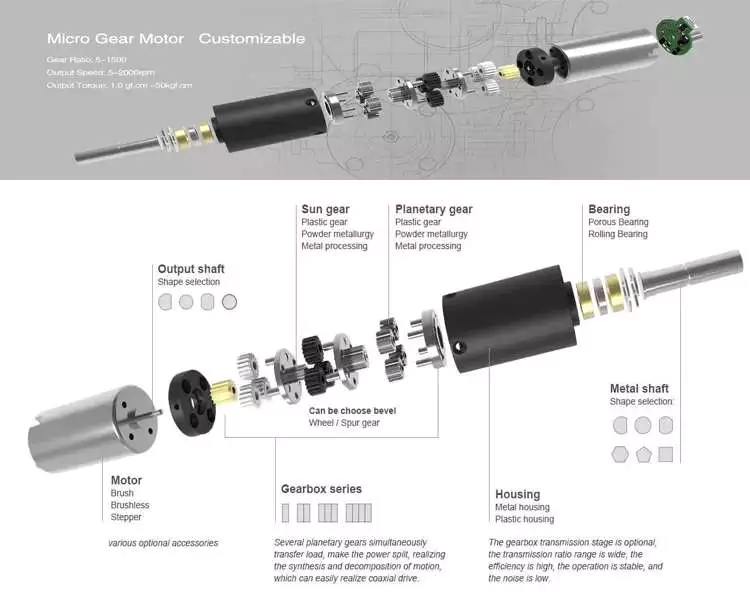
High efficiency
A planetary gearbox is a type of mechanical device that is used for high-torque transmission. This gearbox is made of multiple pairs of gears. Large gears on the output shaft mesh with small gears on the input shaft. The ratio between the big and small gear teeth determines the transmittable torque. High-efficiency planetary gearheads are available for linear motion, axial loads, and sterilizable applications.
The AG2400 high-end gear unit series is ideally matched to Beckhoff’s extensive line of servomotors and gearboxes. Its single-stage and multi-stage transmission ratios are highly flexible and can be matched to different robot types. Its modified lubrication helps it operate in difficult operating conditions. These high-performance gear units are available in a wide range of sizes.
A planetary gear motor can be made of steel, nickel-steel, or brass. In addition to steel, some models use plastic. The planetary gears share work between multiple gears, making it easy to transfer high amounts of power without putting a lot of stress on the gears. The gears in a planetary gear motor are held together by a movable arm. High-efficiency planetary gear motors are more efficient than traditional gearmotors.
While a planetary gear motor can generate torque, it is more efficient and cheaper to produce. The planetary gear system is designed with all gears operating in synchrony, minimizing the chance of a single gear failure. The efficiency of a planetary gearmotor makes it a popular choice for high-torque applications. This type of motor is suitable for many applications, and is less expensive than a standard geared motor.
The planetary gearbox is a combination of a planetary type gearbox and a DC motor. The planetary gearbox is compact, versatile, and efficient, and can be used in a wide range of industrial environments. The planetary gearbox with an HN210 DC motor is used in a 22mm OD, PPH, and ph configuration with voltage operating between 6V and 24V. It is available in many configurations and can be custom-made to meet your application requirements.
High cost
In general, planetary gearmotors are more expensive than other configurations of gearmotors. This is due to the complexity of their design, which involves the use of a central sun gear and a set of planetary gears which mesh with each other. The entire assembly is enclosed in a larger internal tooth gear. However, planetary motors are more effective for higher load requirements. The cost of planetary motors varies depending on the number of gears and the number of planetary gears in the system.
If you want to build a planetary gearbox, you can purchase a gearbox for the motor. These gearboxes are often available with several ratios, and you can use any one to create a custom ratio. The cost of a gearbox depends on how much power you want to move with the gearbox, and how much gear ratio you need. You can even contact your local FRC team to purchase a gearbox for the motor.
Gearboxes play a major role in determining the efficiency of a planetary gearmotor. The output shafts used for this type of motor are usually made of steel or nickel-steel, while those used in planetary gearboxes are made from brass or plastic. The former is the most durable and is best for applications that require high torque. The latter, however, is more absorbent and is better at holding lubricant.
Using a planetary gearbox will allow you to reduce the input power required for the stepper motor. However, this is not without its downsides. A planetary gearbox can also be replaced with a spare part. A planetary gearbox is inexpensive, and its spare parts are inexpensive. A planetary gearbox has low cost compared to a planetary motor. Its advantages make it more desirable in certain applications.
Another advantage of a planetary gear unit is the ability to handle ultra-low speeds. Using a planetary gearbox allows stepper motors to avoid resonance zones, which can cause them to crawl. In addition, the planetary gear unit allows for safe and efficient cleaning. So, whether you’re considering a planetary gear unit for a particular application, these gear units can help you get exactly what you need.


editor by czh 2023-02-19
China Fuji ac servo motor GYS751D5-RB2 750w ac servo motor with Hot selling
Guarantee: 1year
Design Number: GYS751D5-RB2
AC Voltage: 104v
Merchandise Identify: GYS751D5-RB2
Rated Electricity: 750w
Rated Voltage: 104v
Application: CNC
Model: Fuji
Certification: CCC,CE
Rated recent: 4.8A
Pace: 3000rpm
Specification
| Warranty | 1year |
| Place of Origin | Japan |
| Brand | fuji |
| Model Amount | GYS751D5-RB2 |
| Certification | CCC, ce |
| Rated Power | 750w |
| Voltage | 104v |
| Application | CNC |
What Is a Gear Motor?
A gear motor is an electric motor coupled with a gear train. It uses either DC or AC power to achieve its purpose. The primary benefit of a gear reducer is its ability to multiply torque while maintaining a compact size. The trade-off of this additional torque comes in the form of a reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, proper gear technology and ratios provide optimum output and speed profiles. This type of motor unlocks the full potential of OEM equipment.
Inertial load
Inertial load on a gear motor is the amount of force a rotating device produces due to its inverse square relationship with its inertia. The greater the inertia, the less torque can be produced by the gear motor. However, if the inertia is too high, it can cause problems with positioning, settling time, and controlling torque and velocity. Gear ratios should be selected for optimal power transfer.
The duration of acceleration and braking time of a gear motor depends on the type of driven load. An inertia load requires longer acceleration time whereas a friction load requires breakaway torque to start the load and maintain it at its desired speed. Too short a time period can cause excessive gear loading and may result in damaged gears. A safe approach is to disconnect the load when power is disconnected to prevent inertia from driving back through the output shaft.
Inertia is a fundamental concept in the design of motors and drive systems. The ratio of mass and inertia of a load to a motor determines how well the motor can control its speed during acceleration or deceleration. The mass moment of inertia, also called rotational inertia, is dependent on the mass, geometry, and center of mass of an object.
Applications
There are many applications of gear motors. They provide a powerful yet efficient means of speed and torque control. They can be either AC or DC, and the two most common motor types are the three-phase asynchronous and the permanent magnet synchronous servomotor. The type of motor used for a given application will determine its cost, reliability, and complexity. Gear motors are typically used in applications where high torque is required and space or power constraints are significant.
There are two types of gear motors. Depending on the ratio, each gear has an output shaft and an input shaft. Gear motors use hydraulic pressure to produce torque. The pressure builds on one side of the motor until it generates enough torque to power a rotating load. This type of motors is not recommended for applications where load reversals occur, as the holding torque will diminish with age and shaft vibration. However, it can be used for precision applications.
The market landscape shows the competitive environment of the gear motor industry. This report also highlights key items, income and value creation by region and country. The report also examines the competitive landscape by region, including the United States, China, India, the GCC, South Africa, Brazil, and the rest of the world. It is important to note that the report contains segment-specific information, so that readers can easily understand the market potential of the geared motors market.
Size
The safety factor, or SF, of a gear motor is an important consideration when selecting one for a particular application. It compensates for the stresses placed on the gearing and enables it to run at maximum efficiency. Manufacturers provide tables detailing typical applications, with multiplication factors for duty. A gear motor with a SF of three or more is suitable for difficult applications, while a gearmotor with a SF of one or two is suitable for relatively easy applications.
The global gear motor market is highly fragmented, with numerous small players catering to various end-use industries. The report identifies various industry trends and provides comprehensive information on the market. It outlines historical data and offers valuable insights on the industry. The report also employs several methodologies and approaches to analyze the market. In addition to providing historical data, it includes detailed information by market segment. In-depth analysis of market segments is provided to help identify which technologies will be most suitable for which applications.
Cost
A gear motor is an electric motor that is paired with a gear train. They are available in AC or DC power systems. Compared to conventional motors, gear reducers can maximize torque while maintaining compact dimensions. But the trade-off is the reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, when used correctly, a gear motor can produce optimal output and mechanical fit. To understand how a gear motor works, let’s look at two types: right-angle geared motors and inline geared motors. The first two types are usually used in automation equipment and in agricultural and medical applications. The latter type is designed for rugged applications.
In addition to its efficiency, DC gear motors are space-saving and have low energy consumption. They can be used in a number of applications including money counters and printers. Automatic window machines and curtains, glass curtain walls, and banknote vending machines are some of the other major applications of these motors. They can cost up to 10 horsepower, which is a lot for an industrial machine. However, these are not all-out expensive.
Electric gear motors are versatile and widely used. However, they do not work well in applications requiring high shaft speed and torque. Examples of these include conveyor drives, frozen beverage machines, and medical tools. These applications require high shaft speed, so gear motors are not ideal for these applications. However, if noise and other problems are not a concern, a motor-only solution may be the better choice. This way, you can use a single motor for multiple applications.
Maintenance
Geared motors are among the most common equipment used for drive trains. Proper maintenance can prevent damage and maximize their efficiency. A guide to gear motor maintenance is available from WEG. To prevent further damage, follow these maintenance steps:
Regularly check electrical connections. Check for loose connections and torque them to the recommended values. Also, check the contacts and relays to make sure they are not tangled or damaged. Check the environment around the gear motor to prevent dust from clogging the passageway of electric current. A proper maintenance plan will help you identify problems and extend their life. The manual will also tell you about any problems with the gearmotor. However, this is not enough – it is important to check the condition of the gearbox and its parts.
Conduct visual inspection. The purpose of visual inspection is to note any irregularities that may indicate possible problems with the gear motor. A dirty motor may be an indication of a rough environment and a lot of problems. You can also perform a smell test. If you can smell a burned odor coming from the windings, there may be an overheating problem. Overheating can cause the windings to burn and damage.
Reactive maintenance is the most common method of motor maintenance. In this type of maintenance, you only perform repairs if the motor stops working due to a malfunction. Regular inspection is necessary to avoid unexpected motor failures. By using a logbook to document motor operations, you can determine when it is time to replace the gear motor. In contrast to preventive maintenance, reactive maintenance requires no regular tests or services. However, it is recommended to perform inspections every six months.


editor by czh 2023-02-18
China Delta AC Servo Motor and Drive 220v 2000RPM 1.5 kw 1500w ASD-B2-1521-F brushless motor
Error:获取返回内容失败,
Your session has expired. Please reauthenticate.
Benefits of a Planetary Motor
If you’re looking for an affordable way to power a machine, consider purchasing a Planetary Motor. These units are designed to provide a massive range of gear reductions, and are capable of generating much higher torques and torque density than other types of drive systems. This article will explain why you should consider purchasing one for your needs. And we’ll also discuss the differences between a planetary and spur gear system, as well as how you can benefit from them.
planetary gears
Planetary gears in a motor are used to reduce the speed of rotation of the armature 8. The reduction ratio is determined by the structure of the planetary gear device. The output shaft 5 rotates through the device with the assistance of the ring gear 4. The ring gear 4 engages with the pinion 3 once the shaft is rotated to the engagement position. The transmission of rotational torque from the ring gear to the armature causes the motor to start.
The axial end surface of a planetary gear device has two circular grooves 21. The depressed portion is used to retain lubricant. This lubricant prevents foreign particles from entering the planetary gear space. This feature enables the planetary gear device to be compact and lightweight. The cylindrical portion also minimizes the mass inertia. In this way, the planetary gear device can be a good choice for a motor with limited space.
Because of their compact footprint, planetary gears are great for reducing heat. In addition, this design allows them to be cooled. If you need high speeds and sustained performance, you may want to consider using lubricants. The lubricants present a cooling effect and reduce noise and vibration. If you want to maximize the efficiency of your motor, invest in a planetary gear hub drivetrain.
The planetary gear head has an internal sun gear that drives the multiple outer gears. These gears mesh together with the outer ring that is fixed to the motor housing. In industrial applications, planetary gears are used with an increasing number of teeth. This distribution of power ensures higher efficiency and transmittable torque. There are many advantages of using a planetary gear motor. These advantages include:
planetary gearboxes
A planetary gearbox is a type of drivetrain in which the input and output shafts are connected with a planetary structure. A planetary gearset can have three main components: an input gear, a planetary output gear, and a stationary position. Different gears can be used to change the transmission ratios. The planetary structure arrangement gives the planetary gearset high rigidity and minimizes backlash. This high rigidity is crucial for quick start-stop cycles and rotational direction.
Planetary gears need to be lubricated regularly to prevent wear and tear. In addition, transmissions must be serviced regularly, which can include fluid changes. The gears in a planetary gearbox will wear out with time, and any problems should be repaired immediately. However, if the gears are damaged, or if they are faulty, a planetary gearbox manufacturer will repair it for free.
A planetary gearbox is typically a 2-speed design, but professional manufacturers can provide triple and single-speed sets. Planetary gearboxes are also compatible with hydraulic, electromagnetic, and dynamic braking systems. The first step to designing a planetary gearbox is defining your application and the desired outcome. Famous constructors use a consultative modeling approach, starting each project by studying machine torque and operating conditions.
As the planetary gearbox is a compact design, space is limited. Therefore, bearings need to be selected carefully. The compact needle roller bearings are the most common option, but they cannot tolerate large axial forces. Those that can handle high axial forces, such as worm gears, should opt for tapered roller bearings. So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of a helical gearbox?
planetary gear motors
When we think of planetary gear motors, we tend to think of large and powerful machines, but in fact, there are many smaller, more inexpensive versions of the same machine. These motors are often made of plastic, and can be as small as six millimeters in diameter. Unlike their larger counterparts, they have only one gear in the transmission, and are made with a small diameter and small number of teeth.
They are similar to the solar system, with the planets rotating around a sun gear. The planet pinions mesh with the ring gear inside the sun gear. All of these gears are connected by a planetary carrier, which is the output shaft of the gearbox. The ring gear and planetary carrier assembly are attached to each other through a series of joints. When power is applied to any of these members, the entire assembly will rotate.
Compared to other configurations, planetary gearmotors are more complicated. Their construction consists of a sun gear centered in the center and several smaller gears that mesh with the central sun gear. These gears are enclosed in a larger internal tooth gear. This design allows them to handle larger loads than conventional gear motors, as the load is distributed among several gears. This type of motor is typically more expensive than other configurations, but can withstand the higher-load requirements of some machines.
Because they are cylindrical in shape, planetary gear motors are incredibly versatile. They can be used in various applications, including automatic transmissions. They are also used in applications where high-precision and speed are necessary. Furthermore, the planetary gear motor is robust and is characterized by low vibrations. The advantages of using a planetary gear motor are vast and include:
planetary gears vs spur gears
A planetary motor uses multiple teeth to share the load of rotating parts. This gives planetary gears high stiffness and low backlash – often as low as one or two arc minutes. These characteristics are important for applications that undergo frequent start-stop cycles or rotational direction changes. This article discusses the benefits of planetary gears and how they differ from spur gears. You can watch the animation below for a clearer understanding of how they operate and how they differ from spur gears.
Planetary gears move in a periodic manner, with a relatively small meshing frequency. As the meshing frequency increases, the amplitude of the frequency also increases. The amplitude of this frequency is small at low clearance values, and increases dramatically at higher clearance levels. The amplitude of the frequency is higher when the clearance reaches 0.2-0.6. The amplitude increases rapidly, whereas wear increases slowly after the initial 0.2-0.6-inch-wide clearance.
In high-speed, high-torque applications, a planetary motor is more effective. It has multiple contact points for greater torque and higher speed. If you are not sure which type to choose, you can consult with an expert and design a custom gear. If you are unsure of what type of motor you need, contact Twirl Motor and ask for help choosing the right one for your application.
A planetary gear arrangement offers a number of advantages over traditional fixed-axis gear system designs. The compact size allows for lower loss of effectiveness, and the more planets in the gear system enhances the torque density and capacity. Another benefit of a planetary gear system is that it is much stronger and more durable than its spur-gear counterpart. Combined with its many advantages, a planetary gear arrangement offers a superior solution to your shifting needs.
planetary gearboxes as a compact alternative to pinion-and-gear reducers
While traditional pinion-and-gear reducer design is bulky and complex, planetary gearboxes are compact and flexible. They are suitable for many applications, especially where space and weight are issues, as well as torque and speed reduction. However, understanding their mechanism and working isn’t as simple as it sounds, so here are some of the key benefits of planetary gearing.
Planetary gearboxes work by using two planetary gears that rotate around their own axes. The sun gear is used as the input, while the planetary gears are connected via a casing. The ratio of these gears is -Ns/Np, with 24 teeth in the sun gear and -3/2 on the planet gear.
Unlike traditional pinion-and-gear reducer designs, planetary gearboxes are much smaller and less expensive. A planetary gearbox is about 50% smaller and weighs less than a pinion-and-gear reducer. The smaller gear floats on top of three large gears, minimizing the effects of vibration and ensuring consistent transmission over time.
Planetary gearboxes are a good alternative to pinion-and-gear drive systems because they are smaller, less complex and offer a higher reduction ratio. Their meshing arrangement is similar to the Milky Way, with the sun gear in the middle and two or more outer gears. They are connected by a carrier that sets their spacing and incorporates an output shaft.
Compared to pinion-and-gear reduces, planetary gearboxes offer higher speed reduction and torque capacity. As a result, planetary gearboxes are small and compact and are often preferred for space-constrained applications. But what about the high torque transfer? If you’re looking for a compact alt


editor by czh 2023-02-18